12 SNMP
Clixon supports SNMP for retreiving and setting values via netsnmp using a MIB-YANG mapping defined in RFC6643.
12.1 Architecture
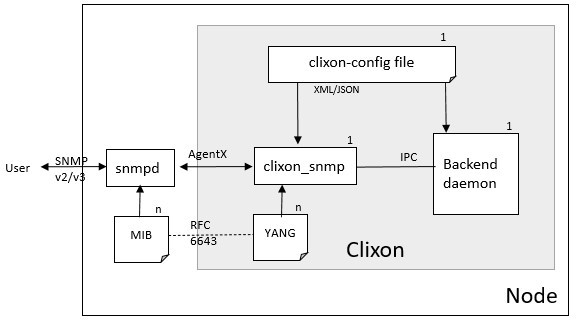
The SNMP frontend acts as an intermediate daemon between the Net-SNMP daemon (snmpd) and the Clixon backend. Clixon-snmp communicates over the AgentX protocol to snmpd typically via a UNIX socket, and over the internal IPC protocol to the Clixon backend.
Clixon-snmp implements RFC 6643 Translation of Structure of Management Information Version 2 (SMIv2) MIB Modules to YANG Modules. The RFC defines how a MIB is translated to YANG using extensions that define a mapping between YANG statements and SMI object IDs and types in the MIB.
In principle, it is also possible to construct a MIB from YANG using the same method, although this is more limited and may involve manual work.
A user can then communicate with snmpd using any of the SNMP v2/v3 tools, such as snmpget, snmpwalk and others.
Note
SNMP support is introduced in Clixon version 5.8
12.2 Configuration
12.2.1 Net-SNMP
Note
Use Net-SNMP version 5.9 or later
To set up AgentX communication between clixon_snmp and snmpd a
Unix or TCP socket is configured. This socket is also configured in
Clixon (see below). An example /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf is as follows:
master agentx
agentaddress 127.0.0.1,[::1]
rwcommunity public localhost
agentXSocket unix:/var/run/snmp.sock
agentxperms 777 777
It is necessary to ensure snmpd does not to load modules implemented by Clixon. For example, if Clixon implements the IF-MIB and system MIBs, snmpd should not load those modules. This can be done using the “-I” flag and prepending a “-” before each module:
-I -ifTable -I -system_mib -I -sysORTable
Further, Clixon itself does not start netsnmp itself, you need to ensure that netsnmp is running when clixon_snmp is started. Likewise, if snmpd is restarted, clixon_snmp must also be restarted.
Note
Net-snmp must be started via systemd or some other external mechanism before clixon_snmp is started.
12.2.2 Clixon
To build the snmp support, netsnmp is enabled at configure time. Two configure options are added for SNMP:
--enable-netsnmpEnable SNMP support.--with-mib-generated-yang-dirFor tests: Directory of generated YANG specs (default: $prefix/share/mibyang)
Then type “make” to build the “clixon_snmp” executable and “make install” to install.
12.2.3 clixon_snmp command line options
$ clixon_snmp -h
usage:clixon_snmp
where options are
-h Help
-V Show version and exit
-D <level> Debug level
-f <file> Configuration file (mandatory)
-l (e|o|s|f<file>) Log on std(e)rr, std(o)ut, (s)yslog(default), (f)ile
-C <format> Dump configuration options on stdout after loading and exit. Format is one of xml|json|text
-z Kill other clixon_snmp daemon and exit
-o "<option>=<value>" Give configuration option overriding config file (see clixon-config.yang)
12.2.4 clixon_snmp configuration
There are two SNMP related options in the Clixon configuration:
- CLICON_SNMP_AGENT_SOCK
String description of the AgentX socket that clixon_snmp listens to.
- CLICON_SNMP_MIB
Names of MIBs that are used by clixon_snmp.
Example:
<CLICON_SNMP_AGENT_SOCK>unix:/var/run/snmp.sock</CLICON_SNMP_AGENT_SOCK>
<CLICON_SNMP_MIB>IF-MIB</CLICON_SNMP_MIB>
Note that the socket /var/run/snmp.sock is the same as configured
in “snmpd.conf” above.
12.3 MIB mapping
Clixon registers MIBs with netsnmp by using YANG specifications. To achieve this, the MIB is first converted (according to RFC6643) to YANG format.
12.3.1 Generating YANG
MIB to YANG conversion can be done using the smidump tool, version 0.5 or later. Manual
mapping is also possible. In Debian smidump is available in the
package “smitools”. You may also find existing repos with converted MIBs.
To convert a MIB to YANG, invoke smidump with the “-f yang” flag
and point it to a MIB. MIBs will usually be in the directory
“/usr/share/snmp/mibs/”:
$ smidump -f yang /usr/share/snmp/mibs/IF-MIB.txt > IF-MIB.yang
Note
smidump 0.5 or later must be used
Once a MIB is converted to YANG, two things should be done:
The YANG is registered as an SNMP module using the
CLICON_SNMP_MIBconfiguration optionThe YANG file must be placed so that it can be found using the regular Clixon YANG finding mechanism, as described in Finding YANG files
12.3.2 Config vs state
By default, all RFC6643 mappings are config false, ie, no configuration data.
To change to configuration data, a deviation statement is made as the following example illustrates:
deviation "/clixon-types:CLIXON-TYPES-MIB" {
deviate replace {
config true;
}
}
For more info, see Section 11 in RFC 6643.
12.3.3 Types
Scalar types are mapped between SMI and YANG types using RFC6643. All types as used by IF-MIB, System and Entity MIBs are supported.
12.3.4 Tables
SNMP tables are supported for config and state and are mapped to YANG lists. It is possible to get and set individual values either via the SNMP API, or via any of the other CLIXON frontends.
Table indexes can be integers and non-integers. Multiple table indexes are supported.
As an implementation detail, Clixon uses the table abstraction in the netsnmp agent library, not table-data or table-instance.
12.3.5 RowStatus
Clixon supports SMIv2 RowStatus for table handling. Where RowStatus is used, the status of the row is returned and set to either active, notInService or notReady.
When writing the status of the row can be set to either createAndGo, createAndWait, active or destroy.
The rowstatus firled itself and all row values in createAndWait mode uses an internal cache which is held in memory by the clixon snmp agent. This internal cache is flushed to Clixon when setting a row to active, like a “pre-commit phase”. When clixon_snmp is restarted, the cache is cleared.