1 Overview
Clixon is a configuration management framework used by networking devices and other computer systems. Clixon provides a datastore, CLI, NETCONF and RESTCONF interfaces all defined by YANG.
Clixon links:
Most of the projects using Clixon are for networking devices. But Clixon can be used for other YANG-based systems as well due to a modular and pluggable architecture.
Clixon has a transaction mechanism that ensures configuration operations are atomic. It also features a generated interactive command-line interface using CLIgen.
The goal of Clixon is to provide a useful, production-grade, scalable and free YANG based configuration tool.
Clixon is open-source and dual licensed. Either Apache License, Version 2.0 or GNU General Public License Version 2.
1.1 System Architecture
Clixon provides YANG functionality with Netconf, Restconf and CLI that can be integrated with an existing “base system” in several ways. The integrations are:
A plugin integration where clixon handles all user interaction with the base system using backend plugins. This is the _primary_ Clixon usage model.
A client integration where the base system uses clixon for configurations as a “side-car”. There is some ongoing work to make Clixon also work for this usage.
1.1.1 Plugin integration
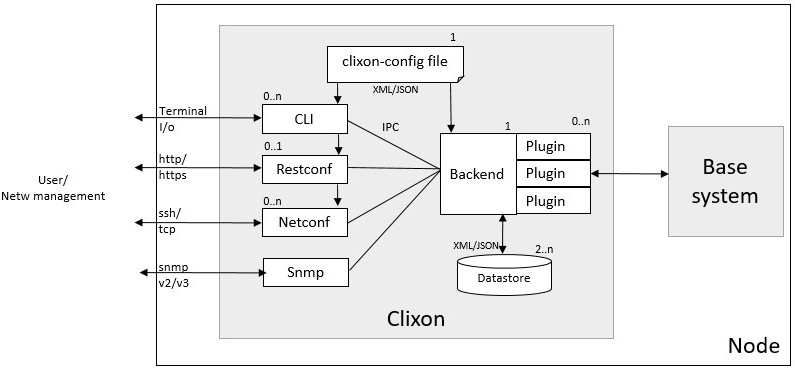
This describes how to integrate a base system with Clixon using plugins.
The Clixon architecture consists of a backend daemon with configuration datastores and a set of internal clients: cli, restconf, netconf and snmp.
The clients provide frontend interfaces to users of the system, such as a Network Management System (NMS) or an interactive human user. The external interfaces include interactive CLI, RESTCONF over HTTP/HTTPS, and XML NETCONF over TCP or SSH. Internally, the clients and backend communicate over an inter-process communication (IPC) bus via NETCONF over a UNIX socket. It is possible to run over an INET socket as well.
The backend manages configuration datastores and implements a transaction mechanism for configuration operations (eg, create, read, update, delete) . The datastore supports candidate, running and startup configurations.
A system integrating Clixon using plugins, typically starts with a set of YANG specifications. Backend plugins are written that interact with the base system. The plugins are written in C using the Clixon API and a set of plugin callbacks. The main callback is a transaction callback, where you specify how configuration changes are made to your system.
You can also design an interactive CLI using CLIgen, where you specify the CLI commands and write CLI plugins. You will have to write CLI rules, but Clixon can generate the configuration part of the CLI, including set, delete, show commands for a specific syntax.
Notifications (streams) are supported both for CLI, NETCONF and RESTCONF clients.
1.1.2 Client integration
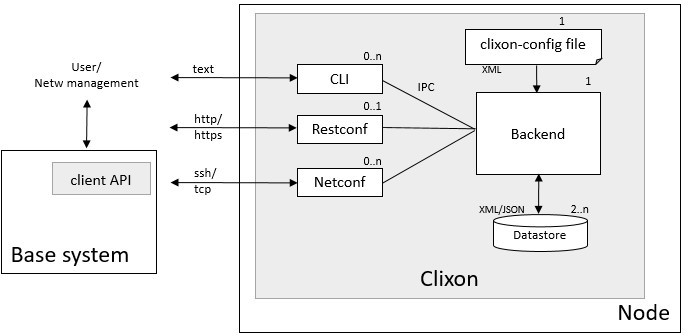
In a client architecture, the base system keeps existing APIs and only YANG-based configurations are exposed via Clixon. The base system acts as a clixon client and uses the clixon client module to subscribe to configuration events using Netconf message passing.
In comparison, the tighter plugin architecture uses dynamically loaded plugins, callbacks and a shared datastore. See clixon client api for more details.
1.2 Platforms
Clixon supports GNU/Linux, FreeBSD and Docker. MacOS may work. Linux platforms include Ubuntu, Alpine, Centos, and Raspian. CPU architectures include x86_64, i686, and ARM32.
1.3 Standards
Clixon supports standards including YANG, NETCONF, RESTCONF, XML and XPath. See Standards section for more details.
1.4 How to get Clixon
Get the Clixon source code from Github:
git clone https://github.com/clicon/clixon.git
1.5 Support
Clixon interaction is best done posting issues, pull requests, or joining the Matrix clixon forum https://matrix.to/#/#clixonforum:matrix.org.
1.6 Bug reports
Report bugs via Github issues
1.7 Reference docs
The user-manual is this document.
For reference documentation of the C-code, Doxygen is used. To build the reference documentation you need to check out the source code, and type make doc, eg:
git clone git@github.com:clicon/clixon.git
cd clixon
./configure
make doc
direct your browser to:
file:///<your home path>/clixon/doc/html/index.html